Hadoop: Writing YARN Applications
- 原生开发YARN应用
- 参考: http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r3.0.0-alpha2/hadoop-yarn/hadoop-yarn-site/WritingYarnApplications.html
- 在YARN上编写一个应用程序,你需要开发Client和ApplicationMaster两个模块,并了解涉及到的几个协议的若干API和参数列表,其中ApplicationMaster还要负责资源申请,任务调度、容错等,总之,整个过程非常复杂。
- 基于Twill开发
- 参考: http://twill.apache.org/GettingStarted.html
- 优点: 简化了YARN开发的复杂性;
- 缺点: 不容易trouble shooting,封装部分不易detect问题,另外也不能支持最新的Hadoop cluster;文档也太少;
- 基于Slider开发
- 参考: http://slider.incubator.apache.org
- 优点: 简化了YARN开发的复杂性;
- 缺点: 不容易trouble shooting,封装部分不易detect问题,另外也不能支持最新的Hadoop cluster;本身的框架也很复杂,
- 基于Spring Hadoop开发
- 参考: https://spring.io/guides/gs/yarn-basic/
- 优点: 简化了YARN开发的复杂性;
- 缺点: 不容易trouble shooting,封装部分不易detect问题,另外也不能支持最新的Hadoop cluster;
开发Client和ApplicationMaster
当用户向YARN中提交一个应用程序后,YARN将分两个阶段运行该应用程序: 第一个阶段是启动ApplicationMaster; 第二个阶段是由ApplicationMaster创建应用程序,为它申请资源,并监控它的整个运行过程,直到运行完成。
1.开发Client启动AM
Client部分是用于将应用提交到YARN, 从而可以启动application master.
客户端通常只需与ResourceManager交互,期间涉及到多个数据结构和一个RPC协议,具体如下: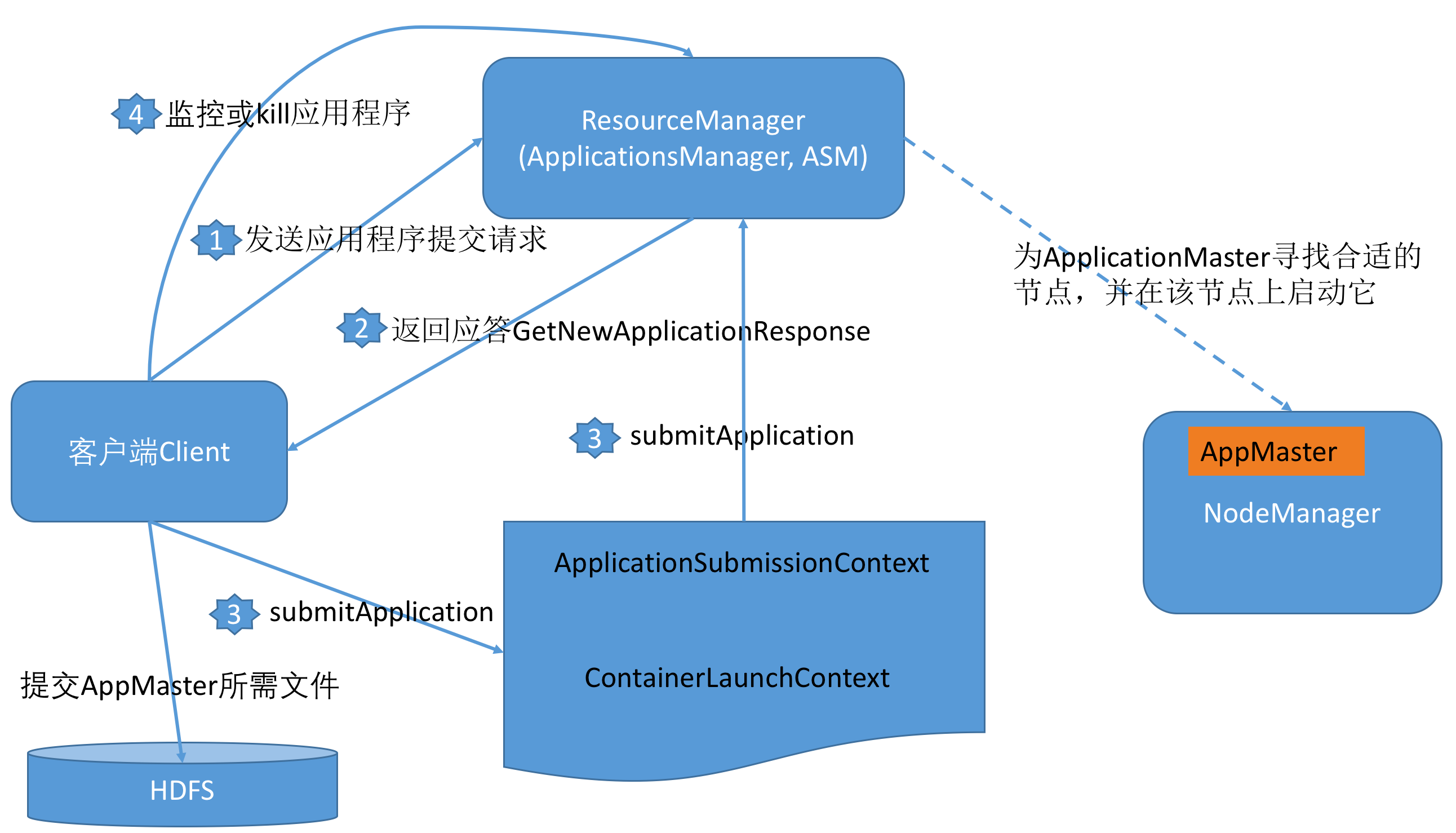
客户端通过RPC协议ApplicationClientProtocol向ResourceManager(也称之为ApplicationsManager、ASM)发送应用程序提交请求GetNewApplicationRequest,ResourceManager为其返回应答GetNewApplicationResponse,该数据结构中包含多种信息,包括ApplicationId、可资源使用上限和下限等。初始化并启动一个yarnClient:
12345YarnClient yarnClient = YarnClient.createYarnClient();yarnClient.init(conf);yarnClient.start();YarnClientApplication app = yarnClient.createApplication();GetNewApplicationResponse appResponse = app.getNewApplicationResponse();Client部分最关键的是构建一个ApplicationSubmissionContext。启动ApplicationMaster所需的所有信息打包到数据结构ApplicationSubmissionContext中,主要包括以下几种信息:
- (1) application id
- (2) application 名称
- (3) application优先级
- (4) application 所属队列
- (5) application 启动用户名
- (6) ApplicationMaster对应的Container信息ContainerLaunchContext,包括:启动ApplicationMaster所需各种文件资源、jar包、环境变量、启动命令、运行ApplicationMaster所需的资源(主要指内存)等。
123456789101112131415// set the application nameApplicationSubmissionContext appContext = app.getApplicationSubmissionContext();ApplicationId appId = appContext.getApplicationId();appContext.setKeepContainersAcrossApplicationAttempts(keepContainers);appContext.setApplicationName(appName);// Set up the container launch context for the application masterContainerLaunchContext amContainer = ContainerLaunchContext.newInstance(localResources, env, commands, null, null, null);// Set up resource type requirements// For now, both memory and vcores are supported, so we set memory and// vcores requirementsResource capability = Resource.newInstance(amMemory, amVCores);appContext.setResource(capability);客户端调用ClientRMProtocol#submitApplication(ApplicationSubmissionContext)将ApplicationMaster提交到ResourceManager上。ResourceManager收到请求后,会为ApplicationMaster寻找合适的节点,并在该节点上启动它。
12LOG.info("Submitting application to ASM");yarnClient.submitApplication(appContext);客户端可通过多种方式查询应用程序的运行状态,其中一种是调用RPC函数ClientRMProtocol#getApplicationReport获取一个应用程序当前运行状况报告,该报告内容包括应用程序名称、所属用户、所在队列、ApplicationMaster所在节点、一些诊断信息、启动时间等。
123456789101112131415161718// Get application report for the appId we are interested inApplicationReport report = yarnClient.getApplicationReport(appId);LOG.info("Got application report from ASM for"+ ", appId=" + appId.getId()+ ", clientToAMToken=" + report.getClientToAMToken()+ ", appDiagnostics=" + report.getDiagnostics()+ ", appMasterHost=" + report.getHost()+ ", appQueue=" + report.getQueue()+ ", appMasterRpcPort=" + report.getRpcPort()+ ", appStartTime=" + report.getStartTime()+ ", yarnAppState=" + report.getYarnApplicationState().toString()+ ", distributedFinalState=" + report.getFinalApplicationStatus().toString()+ ", appTrackingUrl=" + report.getTrackingUrl()+ ", appUser=" + report.getUser());YarnApplicationState state = report.getYarnApplicationState();FinalApplicationStatus dsStatus = report.getFinalApplicationStatus();如果有异常或者其他情况,可以通过yarnClient.killApplication(appId);来kill掉应用;
2.开发ApplicationMaster
ApplicationMaster需要与ResoureManager和NodeManager交互,以申请资源和启动Container,期间涉及到多个数据结构和两个RPC协议。具体步骤如下:
- ApplicationMaster首先需通过RPC协议AMRMProtocol向ResourceManager发送注册请求RegisterApplicationMasterRequest,该数据结构中包含ApplicationMaster所在节点的host、RPC port和TrackingUrl等信息,而ResourceManager将返回RegisterApplicationMasterResponse,该数据结构中包含多种信息,包括该应用程序的ACL列表、可资源使用上限和下限等。
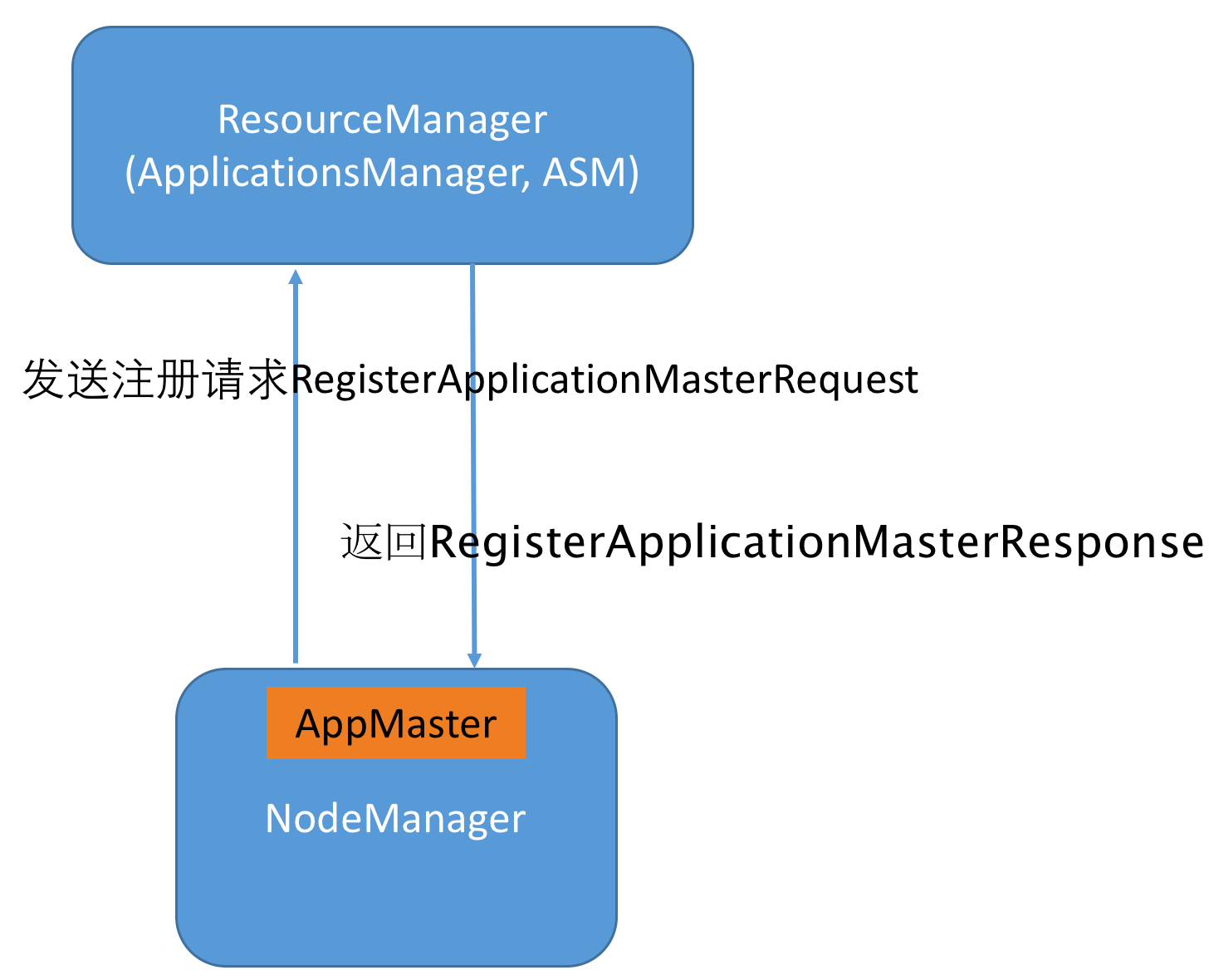
ApplicationMaster与RM之间的心跳:整个运行过程中,ApplicationMaster需通过心跳与ResourceManager保持联系,这是因为,如果一段时间内(默认是10min),ResourceManager未收到ApplicationMaster信息,则认为它死掉了,会重新调度或者让其失败。通常而言,ApplicationMaster周期性调用RPC函数ApplicationMasterProtocol.allocate向其发送空的AllocateRequest请求即可。
构造Container:根据每个任务的资源需求,ApplicationMaster可向ResourceManager申请一系列用于运行任务的Container,ApplicationMaster使用ResourceRequest类描述每个Container(一个container只能运行一个任务):
- 1)Hostname:期望Container所在的节点,如果是*,表示可以为任意节点。
- 2)Resource capability:运行该任务所需的资源量,如(memory/disk/cpu)。
- 3)Priority:任务优先级。一个应用程序中的任务可能有多种优先级,ResourceManager会优先为高优先级的任务分配资源。
- 4)numContainers:符合以上条件的container数目。
- 申请资源分配Container:一旦为任务构造了Container后,ApplicationMaster会使用RPC函数AMRMProtocol#allocate向ResourceManager发送一个AllocateRequest对象,以请求分配这些Container,AllocateRequest中包含以下信息:
- 1)Requested containers:所需的Container列表
- 2)Released containers:有些情况下,比如有些任务在某些节点上失败过,则ApplicationMaster不想再在这些节点上运行任务,此时可要求释放这些节点上的Container。
- 3)Progress update information:应用程序执行进度
- 4)ResponseId:RPC响应ID,每次调用RPC,该值会加1。
- ResourceManager会为ApplicationMaster返回一个AllocateResponse对象,该对象中主要信息包含在AMResponse中:
- 1)reboot:ApplicationMaster是否需要重新初始化.当ResourceManager端出现不一致状态时,会要求对应的ApplicationMaster重新初始化。
- 2)Allocated Containers:新分配的container列表。
- 3)Completed Containers:已运行完成的container列表,该列表中包含运行成功和未成功的Container,ApplicationMaster可能需要重新运行那些未运行成功的Container。
- ApplicationMaster会不断追踪已经获取的container,且只有当需求发生变化时,才允许重新为Container申请资源。
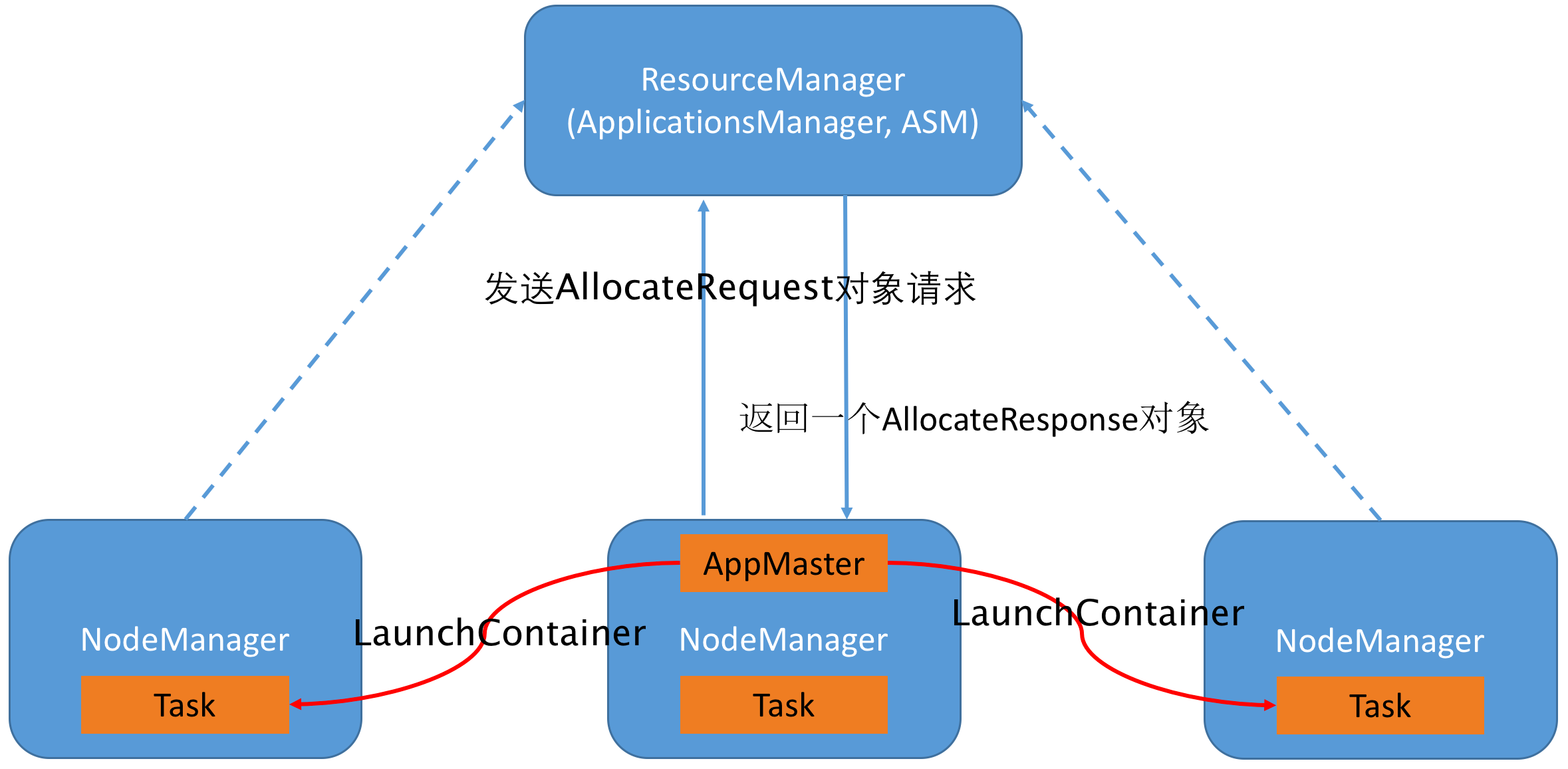
- 启动Container:当ApplicationMaster(从ResourceManager端)收到新分配的Container列表后,会使用ContainerManagementProtocol#startContainer向对应的NodeManager发送ContainerLaunchContext以启动Container,ContainerLaunchContext包含以下内容:
- 1)ContainerId:Container id
- 2)Resource:该Container可使用的资源量(当前仅支持内存)
- 3)User:Container所属用户
- 4)Security tokens:安全令牌,只有持有该令牌才可启动container
- 5)LocalResource:运行Container所需的本地资源,比如jar包、二进制文件、其他外部文件等。
- 6)ServiceData:应用程序可能使用其他外部服务,这些服务相关的数据通过该参数指定。
- 7)Environment:启动container所需的环境变量
- 8)command:启动container的命令
- 监控Container:ApplicationMaster可以通过2种途径监控启动的Container:
- 使用ApplicationMasterProtocol.allocate向ResourceManager发送查询请求;
- 使用ContainerManagementProtocol查询指定的ContainerId对应的Container的状态;
- ApplicationMaster会不断重复前面的步骤,直到所有任务运行成功,此时,它会发送FinishApplicationMasterRequest,以告诉ResourceManage自己运行结束。
基于Twill开发
Apache Twill这个项目则是为简化YARN上应用程序开发而成立的项目,该项目把与YARN相关的重复性的工作封装成库,使得用户可以专注于自己的应用程序逻辑。
下面代码示例是使用Apache Twill开发一个运行在YARN上的helloworld程序:
编译Twill
|
|
启动zookeeper
Start a Zookeeper server instance
This image includes EXPOSE 2181 2888 3888 (the zookeeper client port, follower port, election port respectively), so standard container linking will make it automatically available to the linked containers. Since the Zookeeper “fails fast” it’s better to always restart it.
Run Twill sample
|
|
BundledJarExample Application
The BundledJarExample application demonstrates the Twill functionality that allows you to run any Java application in Twill without worrying about library version conflicts between your application and Hadoop. The example calls the main class in a sample application Echo, which simply logs the command line argument(s) passed to it. The Echo application uses a different version of Guava from Twill and Hadoop distributions. BundledJarExample looks for the dependency in a lib folder packaged at the root of the Echo jar.
You can run the BundleJarExample application from any node of the Hadoop cluster using the below command (be sure to add your ZooKeeper Host and Port):
Slider
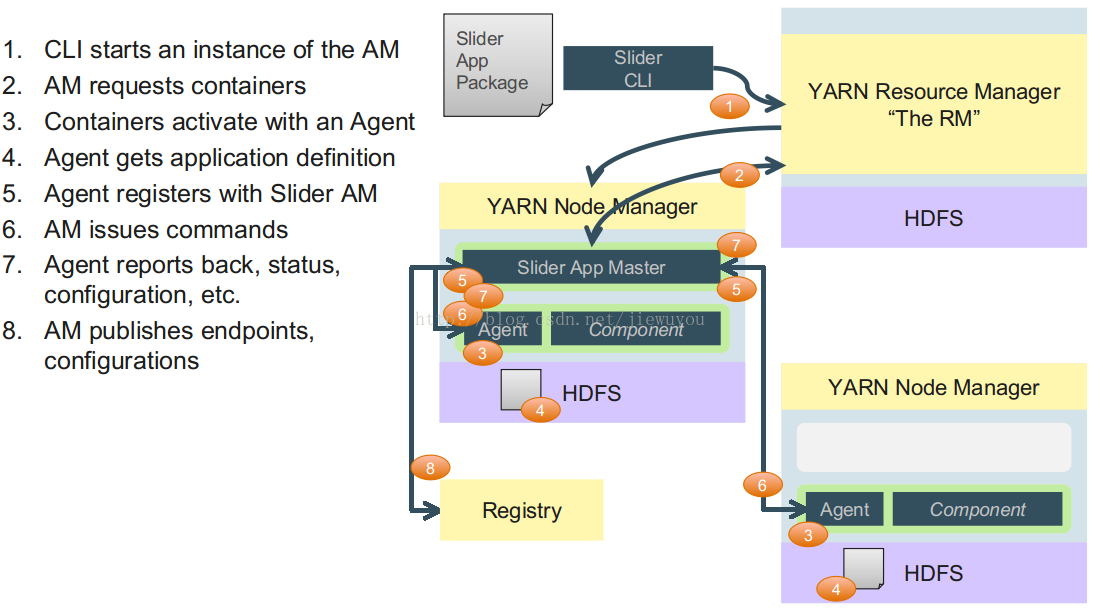
由SliderAM负责给cluster申请资源,并负责容错(component挂掉之后,SliderAM重新找RM申请资源,并进行相应的分配),每个component的实例运行在YARN container中,一个cluster在YARN中的运行流程大致如下:
Spring Hadoop
