分布式配置管理
配置的集中管理:采用consul的KV,将所有微服务的application.properties中的配置内容存入consul。
配置的动态管理:采用archaius,将consul上的配置信息读到spring的PropertySource和archaius的PollResult中,当修改了配置信息后,经常改变的值通过DynamicFactory来获取,不经常改变的值可以通过其他方式获取. 大部分情况下,修改了consul上的配置信息后,相应的项目不需要重启,也会读到最新的值。
Spring Cloud Config
- 集中管理的需求:一个使用微服务架构的应用系统可能会包括成百上千个微服务,因此集中管理很有必要
- 不同环境不同配置:例如数据源在不同的环境(开发,测试,生产)是不同的
- 运行期间可以动态调整。例如根据各个微服务的负载状况,动态调整数据源连接池大小或者熔断阀值,并且调整时不停止微服务
- 配置修改后可以自动更新
Spring Cloud Config主要是为了分布式系统的外部配置提供了服务器端和客户端的支持,只要包括Config Server和Config Client两部分。由于Config Server和Config Client都实现了对Spring Environment和PropertySource抽象的映射,因此Spring Cloud Config很适合spring应用程序。
- Config Server: 是一个看横向扩展的,集中式的配置服务器,它用于集中管理应用程序各个环境下配置,默认使用Git存储配置内容。
- Config Client: 是一个Config Server的客户端,用于操作存储在Config Server上的配置属性,所有微服务都指向Config Server,启动的时候会请求它获取所需要的配置属性,然后缓存这些属性以提高性能。
尽管使用/refresh 端点手动刷新配置,但是如果所有微服务节点的配置都需要手动去刷新的话,那必然是一个繁琐的工作,并且随着系统的不断扩张,会变得越来越难以维护。因此,实现配置的自动刷新是很有必要的,本节我们讨论使用Spring Cloud Bus实现配置的自动刷新。
Spring Cloud Bus提供了批量刷新配置的机制,它使用轻量级的消息代理(例如RabbitMQ、Kafka等)连接分布式系统的节点,这样就可以通过Spring Cloud Bus广播配置的变化或者其他的管理指令。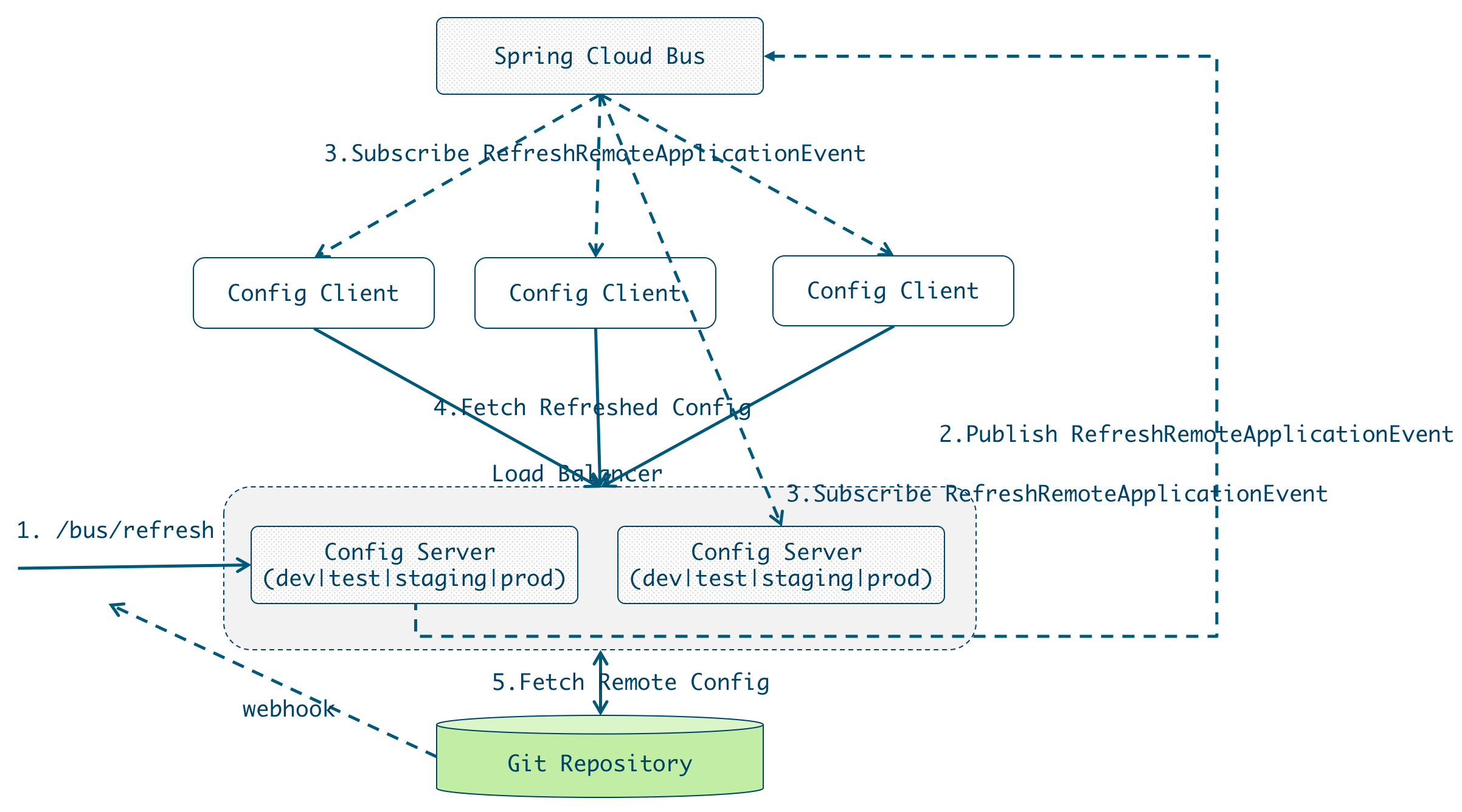
具体操作如下:
启动RabiitMQ:
1docker run -d -p 5671:5671 -p 5672:5672 -p 4369:4369 -p 25672:25672 --hostname my-rabbit --name myrabbit rabbitmqgit clone spring-cloud-config, 我们使用了1.4.1.BUILD-SNAPSHOT;
12cd spring-cloud-config./mvnw install启动config server
12cd spring-cloud-config-server/../mvnw spring-boot:run
查看运行结果:
运行spring-cloud-config-sample
12cd spring-cloud-config-sample../mvnw spring-boot:run查看运行结果:
1curl localhost:8080/configprops
如果出现如下信息,则是需要修改security配置。
在config client/server的yml文件添加:
- curl -X POST localhost:8888/admin/bus/refresh
一旦/bus/refresh被触发,config server会执行如下逻辑:123417:39:18.101 INFO 48866 --- [nio-8888-exec-9] s.c.a.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext : Refreshing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@5e4125d3: startup date [Thu Dec 28 17:39:18 CST 2017]; root of context hierarchy17:39:18.108 INFO 48866 --- [nio-8888-exec-9] o.s.c.c.s.e.NativeEnvironmentRepository : Adding property source: file:/var/folders/zp/kmj0tf897hndh27m457zkzv40000gn/T/config-repo-4824252633476331455/bar.properties17:39:18.108 INFO 48866 --- [nio-8888-exec-9] o.s.c.c.s.e.NativeEnvironmentRepository : Adding property source: file:/var/folders/zp/kmj0tf897hndh27m457zkzv40000gn/T/config-repo-4824252633476331455/application.yml17:39:18.108 INFO 48866 --- [nio-8888-exec-9] s.c.a.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext : Closing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@5e4125d3: startup date [Thu Dec 28 17:39:18 CST 2017]; root of context hierarchy
服务注册与发现
- Consul
- Eureka | Zookeeper | etcd 对比
- Kubernetes Service
分布式锁
负载平衡
- Netflix Ribbon(Spring Cloud)
API网关与智能路由
- Netflix Zuul(SpringCloud)
- Kubernetes Service
分布式服务弹性与容错
- 弹性服务
- 服务降级
- 线程池/信号隔离
快速解决依赖隔离
日志管理
- ELK Stack(LogStash -> ES -> Kibana)
分布式跟踪
- Zipkin
SpringCloud Sleuth
Zipkin is a distributed tracing system. It helps gather timing data needed to troubleshoot latency problems in microservice architectures. It manages both the collection and lookup of this data. Zipkin’s design is based on the Google Dapper paper.
Applications are instrumented to report timing data to Zipkin. The Zipkin UI also presents a Dependency diagram showing how many traced requests went through each application. If you are troubleshooting latency problems or errors, you can filter or sort all traces based on the application, length of trace, annotation, or timestamp. Once you select a trace, you can see the percentage of the total trace time each span takes which allows you to identify the problem application.
监控与度量
Application/Infrastructure monitoring using StatsD + Graphite + Grafana
服务安全
- SpringCloud Security
Auto Scaling
打包部署和调度部署
- Spring Boot;
- Docker/Rkt、Kubernetes Scheduler&Deployment
任务工作管理
- Spring Batch
- Kubernetes Jobs
分布式存储
持久化 - 分布式文件系统
持久化 - 分布式数据库
- [传统关系型数据库集群,如MySQL Cluster]
- Mongo
- Cassandra,HBase
非持久化 - 分布式缓存/消息系统
- Kafka
- [Redis]